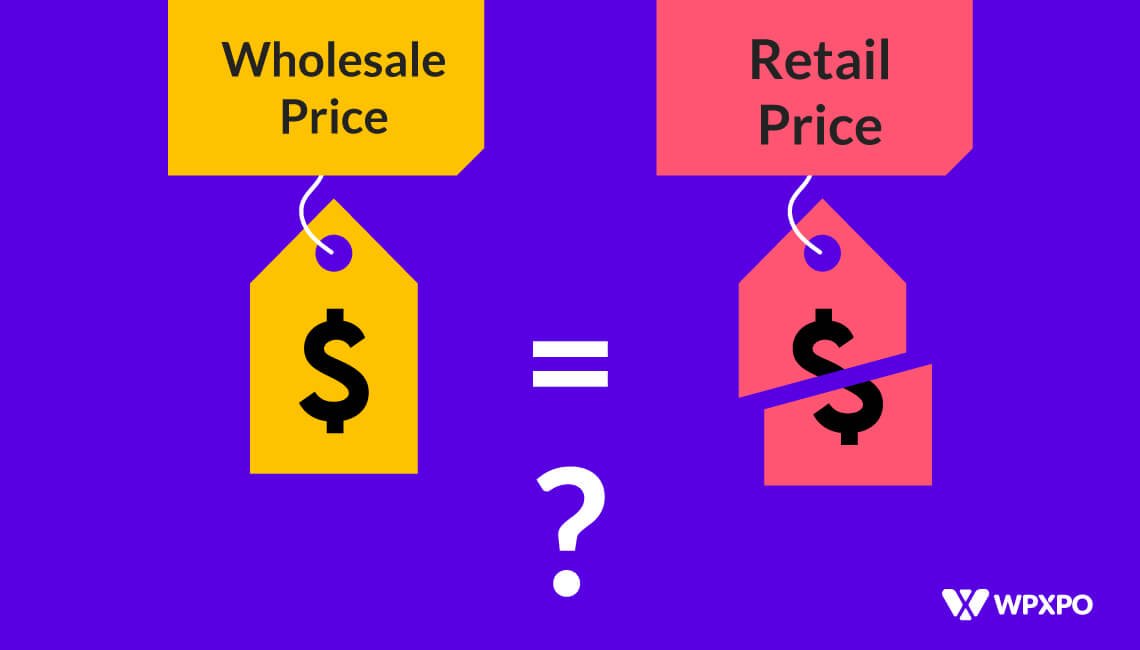
Before creating the perfect wholesale store, you need to dig into many aspects. Price should be the prime concern among all.
Then the common confusion arises. “Is the wholesale price half of retail?”
So, if we give a short explanation, here’s how it goes.
No, the wholesale price is not necessarily half of the retail price. Wholesale price is the price of goods sold to a retailer or other business that will resell the items. Retail price is what customers pay when they purchase the items from the retailer.
The difference between the wholesale price and retail price is the margin that the retailer earns. This margin is determined by various factors, including the cost of the product, the market conditions, the retailer’s overhead costs, and desired profit margin. Therefore, the difference between the wholesale and retail prices may be less than or greater than 50%.
For example, if the wholesale cost of a product is $10 and the retailer wants to earn a 20% profit margin, the retail price will be $12 ($10 + 20% = $12). In this case, the wholesale price is not half the retail price.
This article will give you a thorough outline of wholesale and retail prices. Which will cover the basics and clear your confusion. So, let’s save time by discussing one thing at a time.
What is the Wholesale Price?
The wholesale price is the price that a retailer pays to a manufacturer or distributor for a product before any markups or additional fees. It is typically lower than the retail price. The wholesale price is vital for retailers because it is the price at which they buy the goods. It is also important for manufacturers because it is the price they receive for their products.
The wholesale price is typically based on several factors, including the cost of materials, labor, and overhead. The cost of materials is the cost of the raw materials that go into making the product. The cost of labor is the cost of the people who make the product, such as factory workers and designers. Overhead includes the cost of running the business, such as rent, utilities, and other expenses.
Want some secret wholesale pricing strategies?
Don’t forget to check our ? 25 Secret Wholesale Pricing Strategies ? that will definitely generate sales like you’ve never seen before.
Manufacturers often determine the wholesale price by calculating a markup percentage. This is the percentage by which the cost of materials, labor, and overhead are added to the product’s base cost. For example, if the base cost of a product is $10 and the markup percentage is 25%, the wholesale price would be $12.50.
The wholesale price is also affected by supply and demand. If there is a great demand for a product, the wholesale price may be higher than the base cost. This is because manufacturers want to make as much money as possible on the product. On the other hand, if there is a low demand for a product, the wholesale price may be lower than the base cost. This is because manufacturers want to eliminate the product as quickly as possible.
The price is also affected by competitors. Suppose one manufacturer is selling a product at a lower price than another. In that case, the other manufacturer may lower their wholesale price to remain competitive. This is because they want to make sure that their customers can buy their product at a reasonable price.
Finally, the price is also affected by the manufacturer’s relationship with the retailer. Suppose the retailer and manufacturer have a good relationship. In that case, the manufacturer may offer a lower wholesale price to encourage the retailer to buy more of their product. On the other hand, if the relationship between the retailer and manufacturer is strained, the manufacturer may increase the wholesale price to discourage the retailer from buying their product.
So the price is the price retailers pay to manufacturers and distributors for a product before any markups or additional fees. Factors, including materials, labor, and overhead, determine the wholesale price. It is also affected by supply and demand, competitors, and the relationship between the retailer and manufacturer.
What is the Retail Price?
The retail price of a product is the amount of money a customer pays for it in a store. It is the price a customer pays for the product, excluding any discounts or other incentives a store may offer. The retail price is determined by several factors, including the cost of the product and its associated overhead, the value of the product as perceived by the customer, the current market trends and demand for the product, and the competitive landscape of the product’s niche.
The cost of the product is a significant factor when it comes to determining the retail price. This cost includes the cost of raw materials and labor and the overhead costs associated with production, such as utilities and transportation. The cost of the product is typically the starting point when the retail price is determined.
Market trends and demand for the product also play a role in determining the retail price. If the demand for a product is high, the price of the product is likely to be higher to capitalize on the demand. Similarly, suppose the market trends indicate that a product is decreasing in demand. In that case, the retail price will likely be lower to encourage more customers to purchase the product.
Finally, the competitive landscape of the product’s niche is essential in determining the retail price. If many competitors offer similar products, the retail price may need to be lower to remain competitive. Conversely, if there are few competitors, the retail price may be higher to capitalize on the lack of competition.
So, the retail price of a product is determined by several factors. It includes the cost of the product and its associated overhead, the value of the product as perceived by the customer, the current market trends and demand for the product, and the competitive landscape of the product’s niche. These factors must be considered when determining a product’s retail price.
How to Calculate Wholesale Price
Wholesale pricing is essential for businesses to consider when selling their products. It is the basis for pricing products for resale and is a vital component of a business’s overall pricing strategy. A wholesale price is a business’s cost for a product from a manufacturer or supplier. This cost is then marked up so that retailers can profit when they sell the product to customers. In WooCommerce stores, you can’t do wholesale by default. You have to use plugins like WholesaleX WooCommerce B2B solution to turn your store into a successful B2B business. Here’s a preview of the WholesaleX Dashboard.
Calculating the right wholesale price for a product can be challenging, especially for businesses new to the industry. To accurately price products for resale, businesses must consider a variety of factors. Here are the steps for calculating a wholesale price:
Calculate the Cost of the Product
This includes the cost of the raw materials to make the product, labor costs, and other associated costs such as packaging, shipping, and taxes.
Determine the Desired Profit Margin
This is the percentage of the selling price that will go to the business profit. This should be based on the industry standard, the competitor’s pricing, and the business’s desired profit margin.
Calculate the Wholesale Price
Once the product cost and the desired profit margin have been determined, the wholesale price can be calculated by adding the cost and the desired profit margin.
Adjust the Price as Required
Depending on the product, the market, and the competition, the price may need to be adjusted up or down.
When calculating a wholesale price, businesses must consider a variety of factors. Businesses must be aware of the cost of the product, the desired profit margin, the local market, and the competition. The market and the competition will help determine the price customers are willing to pay for the product. The desired profit margin will help determine the business’s profitability.
Once the cost of the product, the desired profit margin, and the market and competition have been taken into consideration. Businesses can then calculate their wholesale price by adding the cost and the desired profit margin. It is essential to adjust the price to remain competitive and profitable.
Wholesale pricing is essential for businesses to consider when selling their products. By accurately calculating the wholesale price, businesses can ensure that they are charging the right price for their products and maximizing their profitability.
What are the Wholesale Pricing methods?
Wholesale pricing is an integral part of any business. It is crucial to set the correct prices for your products. Several methods can be used to determine the optimal wholesale prices for your products.
Now, we will discuss the different pricing methods available and provide tips on how to price wholesale effectively.
Cost-plus Pricing
The first pricing method that can be used to price wholesale is known as cost-plus pricing. With this method, the cost of the product is the primary factor used to determine the price. This includes the cost of materials, labor, and shipping. The wholesale price is then determined by adding a markup on top of this cost. This markup is typically a percentage of the cost and is used to cover overhead costs and make a profit.
Value-based Pricing
Another pricing method that is commonly used is called value-based pricing. This method determines the product’s price by its perceived value to the customer. This value is based on factors such as the quality of the product, its features, and its brand. This is a helpful method for products where the quality is more important than the cost, as it allows you to set a higher price and make a larger profit.
Competitive Pricing
A third pricing method is called competitive pricing. This method determines the product’s price by comparing it to similar products on the market. Suppose a competitor is selling a similar product at a lower price. In that case, you can price your product competitively to remain competitive. This is a valuable method for products with a lot of competition, as it helps to ensure that you remain competitive in the market.
Market-based Pricing
Finally, another method that can be used to price wholesale is known as market-based pricing. This method takes into account the current supply and demand for the product in the market, as well as the competition. This allows you to adjust the product’s price to reflect the current market conditions.
When pricing wholesale, it is essential to consider all the different methods available and decide which is best for your business. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it is essential to weigh all of them before deciding which one to use. Additionally, it is essential to remember that pricing wholesale is only one part of running a successful business. You should also consider marketing, customer service, and other factors to ensure your business is booming.
There are several different methods you can use to price wholesale effectively. Cost-plus pricing, value-based pricing, competitive pricing, and market-based pricing are all methods that can determine the optimal price for your products.
It is important to consider all these methods before deciding which one to use to ensure that your business is profitable. Additionally, it is essential to remember that pricing wholesale is only one part of running a successful business. Other factors, such as marketing and customer service, should also be considered.
What is the difference between the wholesale price and the retail price?
Wholesale pricing vs retail pricing is another most asked query. The difference between wholesale and retail prices is the difference between what a retailer or wholesaler pays for a product and the price at which that product is sold to the end customer. The difference between the two prices is referred to as the “markup.” In essence, the markup is the extra money that a retailer or wholesaler adds to the cost of an item to make a profit when they sell it.
Wholesale price is the price a wholesaler pays for a product when they buy it in bulk from a manufacturer or distributor. Wholesalers typically buy products in large quantities and can get discounts for buying in bulk. This allows them to profit when they sell the products to retailers.
Retail price is the price at which a retailer sells the product to the end customer. Retailers add their markups to the wholesale prices to cover their costs and make a profit. The markup is usually based on the cost of the product, the retailer’s overhead costs, and the market’s competition.
The amount of markup a retailer or wholesaler adds to the cost of a product is an essential factor in determining the final retail price. The higher the markup, the higher the retail price. In addition, retailers often set their markups based on the cost of the product, the amount of competition in the market, and their profit goals.
The difference between wholesale and retail prices is essential for both businesses and consumers. For businesses, understanding the difference between the two prices is essential for knowing how much profit to make on the products they sell. Understanding the difference between the two prices can help consumers make more informed decisions when shopping for products.
In short, the difference between wholesale and retail prices is the markup that a retailer or wholesaler adds to the cost of a product to make a profit. The markup is usually based on the cost of the product, the amount of competition in the market, and the retailer’s overhead costs. Understanding the difference between the two prices is essential for both businesses and consumers.
Final Thought: Should the Wholesale Price Be Half of the Retail Price?
Whether or not the wholesale price should be half of the retail price is a complex question. There are a variety of factors that must be taken into account when making a pricing strategy for a product. Ultimately, the decision must be based upon a careful analysis of the costs and market conditions.
The wholesale price of goods should reflect the cost of producing them. If the wholesale price is too low, a business may not be able to make a profit; on the other hand, if it is too high, it may need to sell more of the product.
The retail price should reflect the product’s value from the consumer’s perspective. It should be high enough to cover the cost of production and provide a reasonable profit margin. At the same time, it should be low enough to encourage customers to purchase the product.
The wholesale price reflects the cost of the product, while the retail price reflects its value. In some cases, a business may need to charge a higher retail price to make a profit. However, in other cases, it can offer a lower retail price and still make money.
Whether or not the wholesale price should be half of the retail price is a case-by-case question. The pricing strategy of a business should be based on an analysis of the costs, market conditions, and competitive landscape. If a business can charge a price that is both fair to the customer and profitable to the business, then the pricing strategy should be considered successful.
So, far so good, and we think you could use a complete all-in-once solution like WholesaleX for your WooCommerce B2B store.

Conclusion
In conclusion, there are circumstances where a wholesale price is not appropriate to 50% of the retail price. This is because several additional considerations are needed to determine the wholesale price. When determining the wholesale price, it is essential to include the cost of products, the cost of manufacturing, the cost of operation, the cost of marketing and promotion, and any other overhead expenditures. Market competitiveness, product demand, and consumer willingness to pay must all be considered.
You can check out WordPress video tutorials on our YouTube Channel. Also, find us on Facebook and Twitter for regular updates!